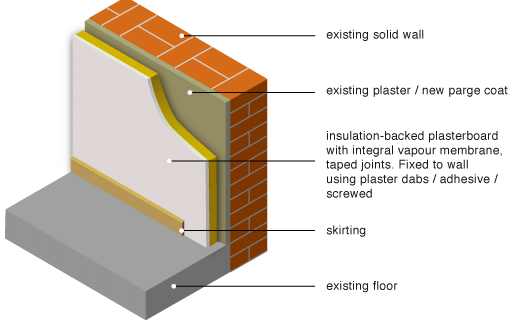
Insulated plasterboards are a popular construction material, made from a combination of gypsumboard or standard drywall board and an insulated sheet put together in a single piece. It comes in various thicknesses and sizes, with a range of material used for both the insulation and the ventilation. Insulated plasterboards are mainly utilized on internal walls to improve the thermal performance of the structure without adding too much structural depth.
One of the most significant differences between insulated and standard plasterboards is their ability to insulate. Standard drywall is not effective at insulating against heat. Gypsum board on the other hand, is effective at preventing heat transfer. Because both materials are primarily used to lower internal temperatures, they have the potential to be used as a heating system, as is the case in combination with radiators. However, it is commonly used as a cooling system.
The thickness of Insulated Plasterboard varies significantly, depending on its composition and the application. The basic insulated plasterboard e.g. EPDM, RTF, SPF is typically thicker than the thermal type. The thermal type is usually less thick, but has a higher R value (thermal resistance) than the EPDM or SPF.
Different thicknesses of Insulated Plasterboard are available to suit varying building applications. The different types of Insulated Plasterboard can either be pre-cut or cut insulated. Pre cut insulation material is generally made of steel, although it also can be made of different types of foam. Pre cut insulated plasterboard can be used in almost any building application that requires bracing and securing together several wooden or metal components together, as long as these components are fastened together with screws and nails.
In addition to using insulated plasterboard as a method for bracing and securing together wooden and metal components, this type of construction material can also be used to create internal walls. One of the advantages of having internal walls created by using this method is that it creates space within an area. This is achieved by the boards splitting to allow air flow through the room or area that is being lined with the material. Although internal wall construction may seem like an easy concept, there are several considerations that need to be taken into account.
Internal walls are most effective at insulating when they are positioned directly against at least two opposite walls. The best situations where this is the most effective include a one inch thick board placed one foot from the bottom of the wall and two to three inches further out along the top of the wall as well. The thickness of the Plasterboard will depend largely on the amount of insulation that will be used inside the room or space that is being lined with the Plasterboard. A thicker model of Plasterboard will generally provide better results at insulating than a thinner one.
There are three different types of Plasterboard that can be used in internal wall applications. The first type of Plasterboard is made out of expanded polystyrene. This type of Plasterboard has a higher density level than the expanded polystyrene which makes it more effective at insulating. Also the thickness of this particular type of Plasterboard will be more along the lines of three inches to six inches. A thicker model of Plasterboard will also generally provide better thermal performance without adding a great amount of depth to the room or space being lined with Plasterboard.
Finally there is also the bonded or laminated plasterboards. When using bonded or laminated Plasterboard it will generally be up to a four inch thickness. This will be an effective and typical thickness for insulating purposes when using a glue. These are the three basic types of Insulated Plasterboard that you can use to make your own wall insulated doors.






